Episode 7
SCALABLE
SOLUTIONS
Due to the increasing demand for data storage and large-scale workloads, driven by artificial intelligence (AI), automation, data analysis and data processing, hyperscale data centres are massive business critical infrastructure.
There is no official definition, but a hyperscale data center should exceed 5,000 servers and 10.000 square feet
(> 900m²). Because of their size, the design is significantly different from most standard data centres.
The volume of data, compute and storage services they process differes signigicantly from regular data centres. Hyperscalers are built to facilitate easy, rapid deployment without reducing performance and efficiency.
Also Colocation data centers need flexible power reservation models and accurate capacity planning to avoid stranded power or space. Although colos traditionally serve diverse tenants, the rising density trend is pushing them toward hyperscale-like characteristics
"With great power comes great responsibility". Therefore metrics such as PUE (power usage effectiveness) are of utmost importance and hyperscale data center aiming for a PUE of 1.1 or 1.0, means perfect efficiency.
Invisible systems like UPS, cooling, and switchgear quickly add up in terms of impact. Neglecting them jeopardizes uptime, efficiency, resilience, and ultimately your ROI.
Modern data centers require tailored heat exchanger solutions to achieve rapid global deployment of innovative systems that reduce power and water usage. Seamless integration of scalable cooling solutions is an important component to ensure an sustainable and reliable operation and reaching the PUE and WUE targets.


200 kW
50 MW+
HVAC SCALE
UTILITY SCALE
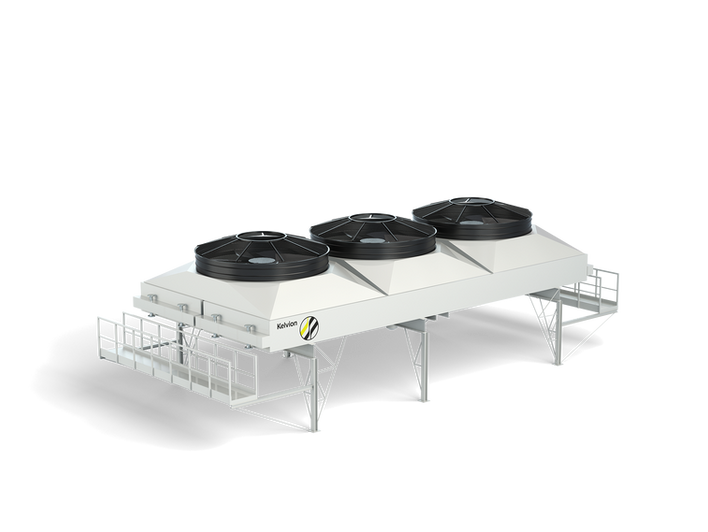
DRY COOLING SOLUTIONS
The next evolution in dry cooling uses large-format units equipped with only a few — but very large — fans. This configuration reduces electrical consumption and lowers maintenance requirements while delivering a high degree of free cooling. When paired with liquid-cooled chillers, these systems achieve exceptional energy efficiency. Such units can be supplied as plug-and-play modules.
For even greater capacity needs, the same platform can be deployed as a scalable system assembled directly on site, enabling tailored solutions for large or complex data center environments. Such systems can be verified by using a digital twin and computational physics to validate design and system integration. This holistic approach ensures accurate performance forecasting, optimized energy efficiency, and reduced development time and costs —critical factors in modern heat-exchange engineering.




Dry Cooler
Giga-Bay®
Mega-Bay®
Mega-Stack
To meet higher thermal demands within a compact footprint, engineered dry coolers with increased heat-exchanger surface area offer a strong advantage. These customized designs maximize heat rejection per square meter and maintain uniform airflow across both upper and lower coil arrays. This ensures stable cooling performance even at elevated loads. Additionally, these systems are designed for rapid deployment and minimal on-site construction effort.
Conventional dry coolers are a proven approach for rejecting heat using ambient air. They remain a reliable choice for moderate heat loads but are beginning to reach their practical limits as rack and power densities continue to rise and metrics like PUE become more and more important.


COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS
Computational physics provides a powerful toolkit for analyzing and optimizing heat-exchange systems by combining advanced numerical methods with engineering insight. Core techniques include Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD), used to simulate fluid flow, turbulence, and thermal performance; and Finite Element Analysis (FEA), applied to evaluate structural behavior, thermal stresses, vibration, and material limits under real operating conditions.
Together, these methods support design validation and system integration, enabling engineers to use a digital twin to verify performance, identify inefficiencies, and assess failure risks well before physical prototypes or systems are built. This holistic approach ensures accurate performance forecasting, optimized energy efficiency, and reduced development time and costs —critical factors in modern heat-exchange engineering.
PRACTICAL EXAMPLE
CFD analysis of the entire 300 MW heat rejection system, taking into account surrounding buildings and the prevailing wind direction.

Dry Coolers
Facility
Thermal modelling of heat rejection equipment, visualizing air path lines with related temperatures.


EVAPORATIVE COOLING SOLUTIONS
There is a significant relationship between the two metrics of effective energy and water usage, especially when it comes to the performance of heat rejection equipment.
At one end of the spectrum are dry coolers which have zero impact on your water consumption yet a high impact on power consumption, whilst on the other end are technologies like cooling towers, which have a comparatively lower impact on power yet a significant impact on water usage.
There are innovative technologies in between, such as adiabatic and hybrid dry coolers, as well as other bridging technologies, which have lower power usage at the expense of water usage and vice versa.
However, there are a number of ways of gaining efficiency, considering all metrics from ambient conditions to water availability and legislation.




Cooling Towers
Hybrid Cooler
Adiabatic Systems
CASCADE COOLING
The future of cooling for hyperscale data centers lies in modular, intelligent, and sustainable concepts.
The key to success is the integration of multiple technologies to achieve maximum efficiency, scalability, and environmental sustainability.
Advanced system designs — engineered around specific operating conditions and site constraints — optimize both water and energy consumption for the application. Such combined solutions enable an innovative combination of dry and wet cooling technologies to deliver unmatched efficiency, operational flexibility, and long-term sustainability.
In cooler months, when ambient temperatures are low, the system operates in dry mode to maximize free cooling potential. During peak summer loads, the wet mode ensures full thermal capacity, while a smart mixed mode bridges the transition to maintain optimal performance year-round.
Whether the priority is energy savings or water conservation, Cascade Cooling Solutions adapt with multiple operating modes – seamlessly and efficiently. It’s a smart, high-performance solution built for high-demanding applications.
MODE VARIANTS

INTEGRATED SOLUTIONS
Hyperscale data centers increasingly support AI, HPC, and other high-performance workloads. These applications require cooling solutions that can handle high thermal design power (TDP). CDU’s are needed to distribute coolant precisely and efficiently and enable liquid cooling, which is significantly more effective than air cooling at removing heat from high-power components like CPUs and GPUs. Innovative CDU solutions are the backbone of high-efficiency liquid cooling strategies in hyperscale data centers, helping operators meet performance, sustainability, and cost goals — while ensuring future readiness.

1
5
4
3
6
7
2
CENTRALIZED COOLING DISTRIBUTION UNIT
A Centralized Cooling Distribution Unit (CCDU) offers data center operators a highly efficient, scalable, and cost-effective alternative to traditional rack-level CDUs. By locating the CCDU outside the whitespace, valuable rack space inside the data hall is preserved, enabling higher IT equipment density and more efficient use of floor space. Its scalable design allows capacity growth without the need to physically modify or expand operational racks, making it ideal for data centers that need to adapt quickly to changing IT loads.
1
PUMPS
Industrial-grade end-suction or inline pumps that are highly efficient and sourced from well-known suppliers with global availability
5
VARIABLE FREQUENCY DRIVES (VFDS)
for intelligent, demand-based speed regulation and optimized energy efficiency.
2
PLATE HEAT EXCHANGERS
Highly efficient plate heat exchanger for close temperature approach and high serviceability
6
INLINE FILTERS
Type of filter (bag, cartridge, basket, y-strainer) depends on the customer specifications and micron rating
3
FRAME
Robust and stable construction under operational stress
7
EXPANSION TANK
for thermal expansion management
4
SENSORS & CONTROLS
PLC-based automation with fault-tolerant redundancy control for seamless pump switchover

Engineered for higher thermal inertia, the CCDU can deliver improved resilience against fluctuating heat loads and support higher volume capacities, ensuring stable operation even under dynamic conditions. Its direct connection to the facility’s chilled water system enhances hydraulic efficiency and simplifies integration into existing cooling infrastructures.
A single CCDU is planned to serve multiple cooling loops and integrates smart monitoring and control in one interface, providing real-time visibility of flow, temperature differentials, and alarms across the entire system. Unlike conventional distributed CDUs – localized systems - redundancy is implemented at the central level, which significantly lowers both CAPEX and OPEX by reducing the number of redundant components required at each rack.
Such solutions could simplifiy installation and control as well as streamline deployment and operation. By consolidating cooling functions, it ensures greater system resiliency and minimizes the duplication of redundancies across multiple units. Additionally, centralized CDUs can contribute to reduced maintenance requirements, making them a smart choice for efficient and reliable thermal management.

Localized Liquid Cooling (< 3 MW)
Centralized Liquid Cooling (> 3 MW)
Facility Loop







RACK COOLING SOLUTIONS
As hyperscale and colocation data centers continue to push the boundaries of compute performance, traditional room-level cooling is reaching its limits. High-density racks, GPU-intensive workloads, and AI-driven architectures demand solutions that can deliver efficiency, precision, and reliability — right where the heat is generated.
Rack-level solutions can be deployed modularly, expanding capacity exactly where it is needed. By removing heat directly at the source, rack-level cooling significantly increases thermal efficiency and eliminates recirculation effects. Innovative cooler designs offer a high level of capacity density and space saving potential in the whitespace. Another benefit is, that no suspended ceiling is needed for such a solution.
This targeted approach reduces the energy needed for air movement without the need for a second floor. Hyperscalers and colocation providers gain flexibility to grow their environments without overprovisioning or adding unnecessary mechanical complexity.
High power density is becoming the new standard. Tailormade designs of coolers enables operators to fully utilize their whitespace and maximize ROI on their data center footprint. Scalability and resiliency is another major benefit.